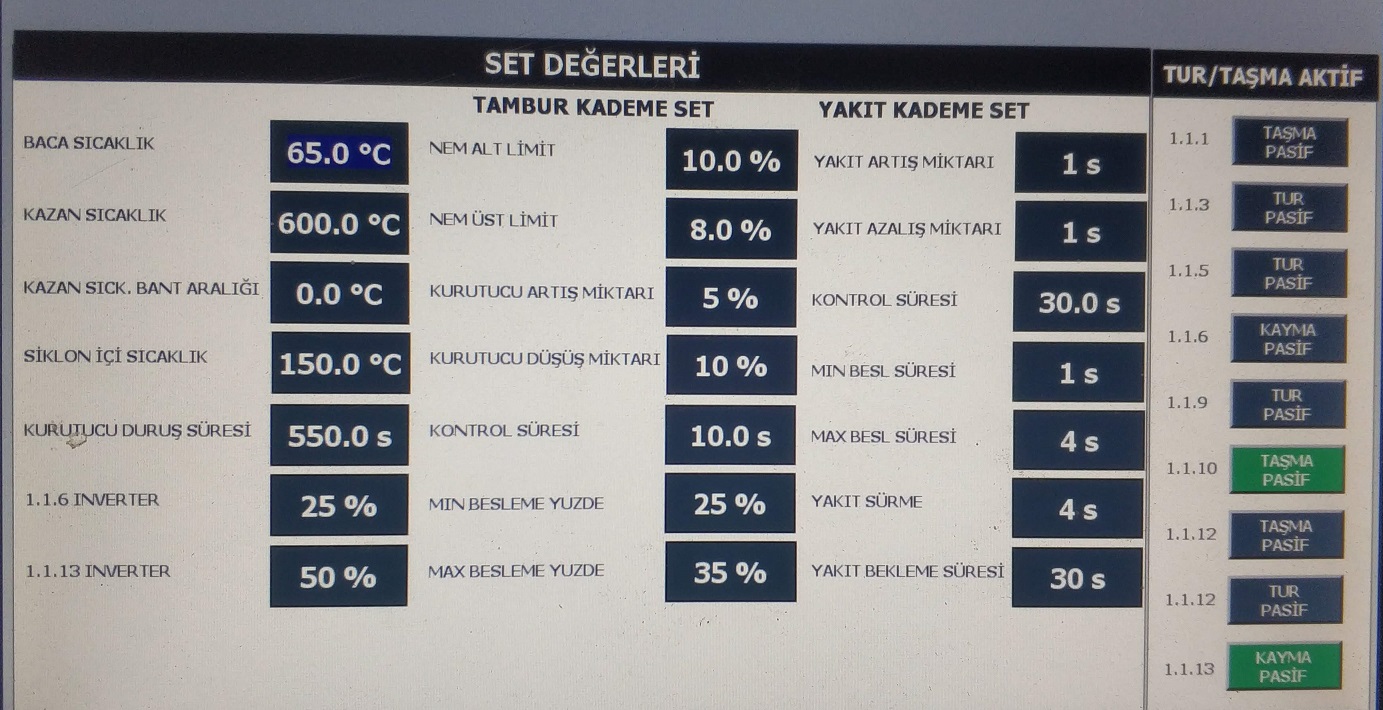
How to Dry Sawdust?
Various types of dryers are used in drying wood sawdust according to the moisture and capacity of the sawdust.
Jet Drying System: It is mostly used in low capacities of below 1 ton / hour and moisture content below 30%. Exceeding the capacity and the limit of drying temperatures are not recommended in this drying system.
Single Pass Drying System: The drum must be long in order to meet the required time (lenght of stay in the drum) for drying the sawdust. For this reason, it is generally not recommended to use this type of dryer for the sawdust drying.
Double Pass Drying System: It is the drying system we recommend for capacities of 1 ton and above up to 5 tons / hour. It is a drying system with high energy efficiency and low production cost.
Three Pass Drying System: It is a drying system we recommend for drying sawdust of 5 tons / hour and above. Because of the three drums are nested, it is one of the most efficient drying systems for drying, and the size of the drying system directly affects the product price.
How is Sawdust Pressed?
In the process of converting sawdust into pellets, the sawdust must be heated to 120-130°C. The heat makes the lignin in the wood sticky and ensures that the pellet is in a more stable and non-breakable form. Then the sawdust is pressed into a disk and the resulting pellets are cut outside the disk.
Cooling Process
Wood pellets come out of the press machine hot and soft. After the cooling process, the pellets harden and lose moisture. Our target temperature after the cooler is between 5-10%.
Is the Drying Process Dangerous?
Thanks to the R&D studies and projects carried out by our company on drying systems, the drying systems we produce eliminate many dangers. However, drying systems manufactured by inexperienced manufacturers and untrained operators pose many risks such as fire and explosion when drying sawdust.
As Yağcı Makina, our advice to our valued customers is to always prioritize the manufacturer’s experience and references when purchasing a drying system.

 English (United Kingdom)
English (United Kingdom)  French (fr-FR)
French (fr-FR)  Turkish (tr-TR)
Turkish (tr-TR)